Raoult's Law شرح - الصف الثالث الثانوي - الفصل الدراسي الأول - كيمياء - ال .... According to this law, the relative lowering of vapour pressure is equal to the ratio of the moles of the solute and the total number of moles in the solution, i.e., the mole fraction of. Both raoult's law and henry's law have a form of an equilibrium constant in which the particles are going from the ideal liquid phase to the ideal gas phase. The pressure at which vapor is formed above a solid or liquid at a particular temperature is called the a solution which strictly obeys raoult's law is known as ideal solution. Raoult's law states that for a solution containing non volatile solute, at a given temperature, the relative lowering of vapour pressure is equal to mole fraction of the solute. Other articles where raoult's law is discussed:
Raoult's law the observation that the vapour in equilibrium with a mixture is richer in the more volatile component is expressed quantitatively as raoult's law. Raoult's law is a phenomenological law that assumes ideal behavior based on the simple microscopic assumption that intermolecular forces between unlike molecules are equal to those between similar. Raoult s law when a solute is dissolved in a solvent, the vapour pressure of the latter is lowered proportionally to the mole fraction of solute present. According to this law, the relative lowering of vapour pressure is equal to the ratio of the moles of the solute and the total number of moles in the solution, i.e., the mole fraction of. Raoult's law relationship between vapor pressure and concentration of a solution tutorial for raoult's law.
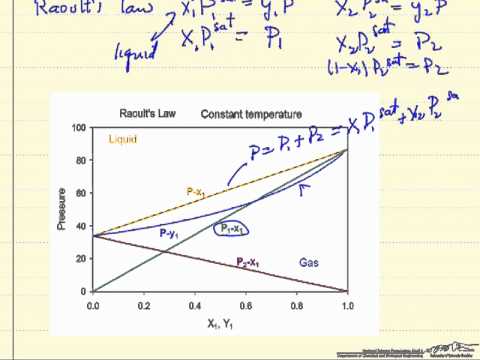
Raoult's law gives a method of estimating the composition and pressure of the vapour above a liquid mixture.
For a solution, raoult's law relates the relative concentrations of the components in solution with their relative vapor pressures above the solution. Raoult's law is a phenomenological law that assumes ideal behavior based on the simple microscopic assumption that intermolecular forces between unlike molecules are equal to those between similar. A french chemist, francois marte raoult gave the relationship between partial pressure and mole fraction of two components. Raoult's law the observation that the vapour in equilibrium with a mixture is richer in the more volatile component is expressed quantitatively as raoult's law. Raoult's law relationship between vapor pressure and concentration of a solution tutorial for raoult's law. The vapor pressure of an ideal solution is dependent on the vapor pressure of each chemical component and the mole fraction of the. Raoult's law for volatile liquids. The relationship is known as raoult's. Raoult's law indicates the behavior of solvent in a solution that is in equilibrium with its vapor pressure. However, there are certain limitations when applying these laws for real solutions. For a solution of two components a (volatile. Raoult's law synonyms, raoult's law pronunciation, raoult's law translation, english dictionary definition of raoult's law. Raoult — may indicate:* in physics, raoult s law on vapor liquid equilibrium.
Quantitatively, raoult's law states that the solvent's vapor pressure in solution is equal to its mole fraction times its vapor pressure as a pure liquid, from which it follows that the freezing point. For a solution, raoult's law relates the relative concentrations of the components in solution with their relative vapor pressures above the solution. …statement of this condition is raoult's law, which …and nonpolar components, deviations from raoult's law diminish as temperature rises. Raoult's law relationship between vapor pressure and concentration of a solution tutorial for raoult's law. Both raoult's law and henry's law have a form of an equilibrium constant in which the particles are going from the ideal liquid phase to the ideal gas phase.

This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the deviations found in raoult's law.
…statement of this condition is raoult's law, which …and nonpolar components, deviations from raoult's law diminish as temperature rises. The vapor pressure and composition in equilibrium with a solution can yield valuable information regarding the thermodynamic properties of the liquids involved. Raoult s law when a solute is dissolved in a solvent, the vapour pressure of the latter is lowered proportionally to the mole fraction of solute present. Raoult — may indicate:* in physics, raoult s law on vapor liquid equilibrium. Raoult's law states that for a solution containing non volatile solute, at a given temperature, the relative lowering of vapour pressure is equal to mole fraction of the solute. when two liquids that are. For a solution of two components a (volatile. This article describes the basis of raoult's law and provides an example of how to apply it. Raoult's law gives a method of estimating the composition and pressure of the vapour above a liquid mixture. For a solution, raoult's law relates the relative concentrations of the components in solution with their relative vapor pressures above the solution. Raoult's law is a phenomenological law that assumes ideal behavior based on the simple microscopic assumption that intermolecular forces between unlike molecules are equal to those between similar. Raoult's law the observation that the vapour in equilibrium with a mixture is richer in the more volatile component is expressed quantitatively as raoult's law. According to this law, the relative lowering of vapour pressure is equal to the ratio of the moles of the solute and the total number of moles in the solution, i.e., the mole fraction of.
Both raoult's law and henry's law have a form of an equilibrium constant in which the particles are going from the ideal liquid phase to the ideal gas phase. The escaping tendency of a solvent is measured by its vapor pressure. ** françois marie raoult, after whom raoult s law is named; Raoult's law is a chemical law that states that the vapor pressure of a solution is dependent on the mole fraction of a solute added to the solution. Raoult's law synonyms, raoult's law pronunciation, raoult's law translation, english dictionary definition of raoult's law.

Raoult's law is a chemical law that states that the vapor pressure of a solution is dependent on the mole fraction of a solute added to the solution.
A rule of conduct or procedure established by custom, agreement. Both raoult's law and henry's law have a form of an equilibrium constant in which the particles are going from the ideal liquid phase to the ideal gas phase. Raoult's law states that a solvent's partial vapour pressure in a solution is equal or the same as the vapour pressure of the pure solvent multiplied by its mole fraction in the solution. Raoult's law for volatile liquids. The escaping tendency of a solvent is measured by its vapor pressure. For a solution of two components a (volatile. ** françois marie raoult, after whom raoult s law is named; The vapor pressure of an ideal solution is dependent on the vapor pressure of each chemical component and the mole fraction of the. Raoult's law gives a method of estimating the composition and pressure of the vapour above a liquid mixture. The relationship is known as raoult's. Raoult's law is a chemical law that states that the vapor pressure of a solution is dependent on the mole fraction of a solute added to the solution. Since deviations from ideal behavior are. Shows how the lowering of vapour pressure affects the boiling point and freezing point of the solvent.
The raoult's law calculator computes vapor pressure where solvent molecules can escape as a gas from a liquid solvent based on the mole fraction of solvent and the initial vapor pressure of solvent raoult. The vapor pressure of an ideal solution is dependent on the vapor pressure of each chemical component and the mole fraction of the.
